Top 50 Solar PV Plants in Emerging Markets
by Marco Dorothal, Solarplaza
We’ve compiled an overview of the top 50 solar PV projects in emerging markets with the purpose of showing the market potential of solar power in developing regions in Asia, Africa and Latin America. Therefore we excluded the more advanced and developed solar markets in Asia (China, India, Japan), North America and Europe. This list of solar PV projects comes in preparation of our 2-day conference, Making Solar Bankable set to be held in Amsterdam on the 15-16th of February, 2018.
Top 10 Operational Solar PV plants in Emerging Markets
| # | Plant Name | Size (MW) | Location | Country | Since | Owner | Developer | Value ($m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park Phase II | 400 | Bahawalpur, Punjab | Pakistan | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 2 | Nova Olinda | 292 | Ribeira do Piauí, Piauí | Brazil | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 3 | Ituverava | 254 | Tabocas do Brejo Velho, Bahia | Brazil | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 4 | El Romero | 246 | Municipality of Vallenar, in the Atacama Region | Chile | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 5 | Solar Capital De Aar | 175 | Northern Cape, De Aar | South Africa | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 6 | Finis Terrae | 160 | Municipality of María Elena in the Antofagasta Region | Chile | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 7 | Lapa Solar Park | 158 | Bom Jesus da Lapa, Bahia | Brazil | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 8 | FV Bolero | 147 | Atacama Desert of Northern Chile | Chile | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 9 | Nacaome and Valle Solar Power Plant | 146 | Nacaome region of the State of Valle | Honduras | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
| 10 | Luz del Norte "Northern Light" | 141 | Copiapó is the nearest city to the site | Chile | X* | X* | X* | X* | |
|
|
|||||||||
The top 3 solar PV plants: Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park, Nova Olinda and Ituverava
In recent years, the benefits of solar power in emerging markets have been continuously growing as a result of economies of scale and cost reduction technologies in the regions. In many cases, the various emerging markets choose to take advantage of market opportunities differently, depending on their regulations and energy policies.
Pakistan
In the Asian region, Pakistan was able to top the list because of their massive Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park, which currently has a capacity of 400 MW. The country has plans to finalize the project in late 2017 by adding an extra 600 MW of capacity to the solar park, altogether amounting to an awe-inspiring 1GW of solar capacity.
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Pakistan has installed around 410 MW of solar capacity in 2016. Besides the giant Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park, the country has been quite active in the solar power market, with 72.5 MW of new solar capacity scheduled to be finalized by the beginning of 2018 and 484 MW expected to be completed by the end of 2019.
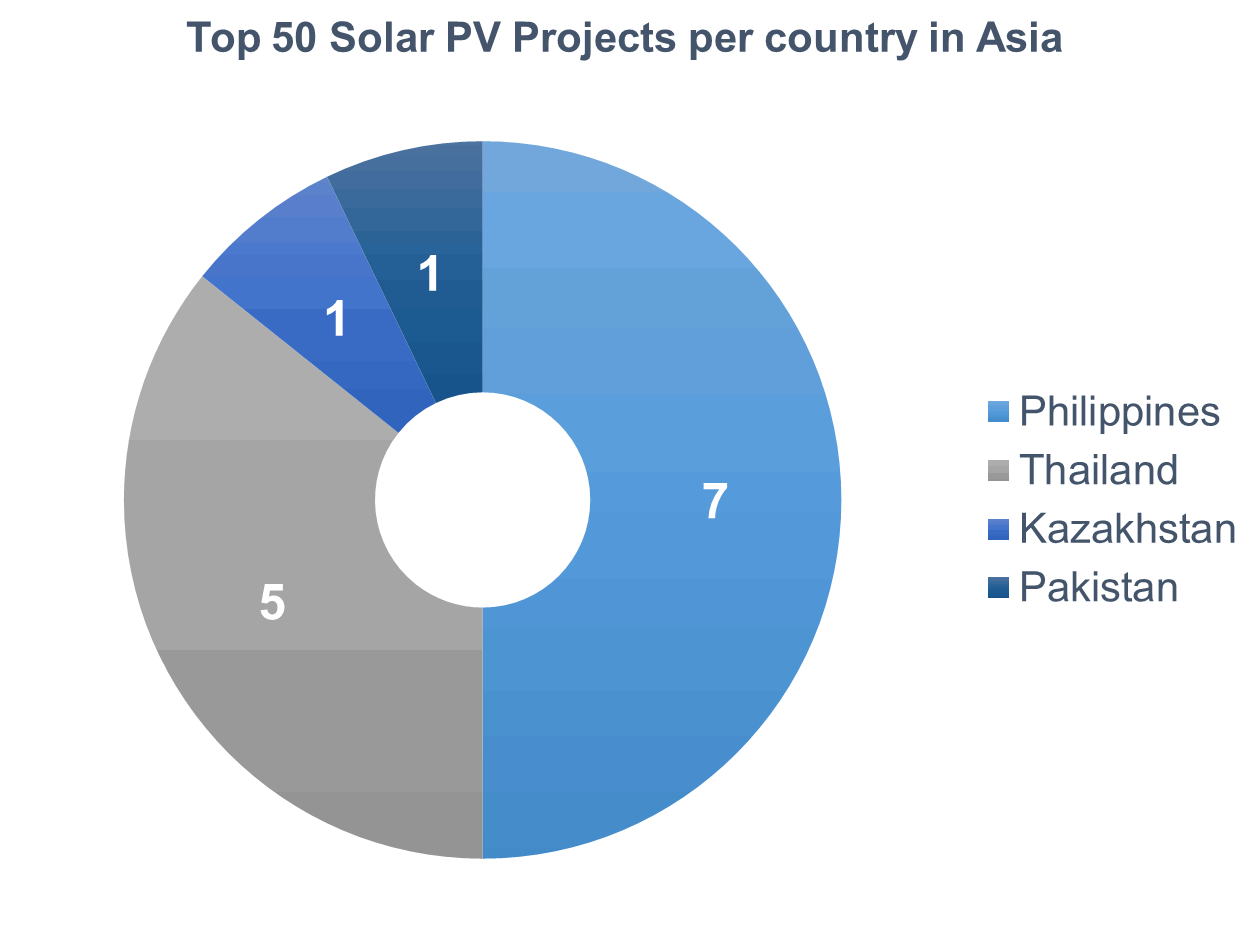
Looking at the total quantity of projects per country, the top ranked emerging markets with the most Top-50 listed operational solar PV projects are South Africa, Chile and the Philippines. We’ll dive deeper into some of the most prolific markets represented in the Top 50.
South Africa
Currently, South Africa has 19 operational solar PV projects that have been ranked in the top 50. When it comes to solar power, this makes it by far the biggest market in Africa, followed by Algeria with its 4 operational solar PV projects ranked on the list. Not only does South Africa have the most amount of solar PV projects in Africa, but they also have the fifth overall largest solar PV project in the emerging markets, namely the ‘De Aar’ solar project. In 2013, the first phase of the project was connected, boasting a capacity of 85 MW. The second phase of the project was finished early this year, adding 90 MW of newly installed capacity, thereby making it the biggest solar PV project in sub-Saharan Africa with a total capacity of 175MW.
A recent report by South Africa’s Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) showed that the South African solar market registered approximately 509 MW of new PV capacity in 2016. This is a result of the significant drop in the price of solar power over the past 5 years. If all of the countries in Africa want to develop low-cost accessible solar PV sites, countries can opt to share power and build transmission lines across borders in order to have a lower environmental impact, while reducing the number of fossil fuel plants that need to be built, according to research conducted by UC Berkeley. International transmission lines are already being planned, but need to incorporate sharing of solar power in order for PV technology to compete with other energy generation technologies.
Source: Acciona - El Romero Solar Chile
Chile
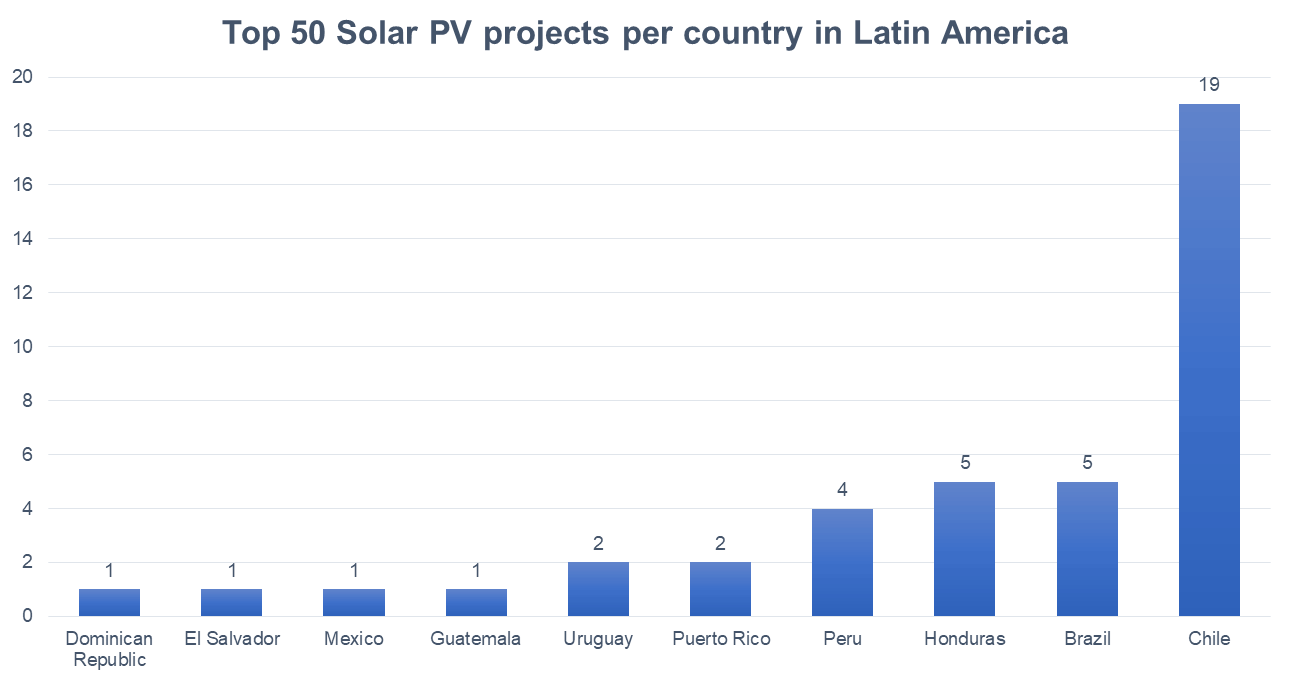
In Latin America, Chile has 19 operational projects ranked in the top 50, making it the second biggest emerging market of operational solar PV projects. Besides having the biggest market, the country also has the third largest operational solar PV plant in Latin America, The El Romero Solar Plant, located in the Atacama Desert. The solar plant was put into operation in November 2016 and has a total capacity of 246 MW. Currently, the plant is completely owned, operated and maintained by Acciona Energy.
In 2016, the U.S. Energy Information Administration stated in their annual international energy outlook that the energy demand for Chile is forecasted to increase with 2.6% annually over the next 20 years, compared to an increase of 0.7% estimated for the US. Additionally, the country has almost 75% of the installed solar capacity in Latin America despite having only 3% of the population.
Nonetheless, one of the factors that critically hinders the development of renewable energy projects in Chile is the fact that the country’s northern, central and southern grids operate independently and are not integrated. The majority of energy demand is located in the south of Chile, while the majority of energy being produced is in the north. In order for Chile to keep up with the growing electricity demand, it will need to expand its transmission links. If the country is able to connect the northern grid to the southern grid, it could allow key solar producers in the northern Atacama area to access customers in the southern areas of Chile. The specifics of the future of Chile’s transmission lines are discussed in more detail our article “Has Chile Fixed Its Transmission Issues?” for our event Solar Asset Management LATAM.
Other Latin American countries that were ranked in our Top 50 list and show significant potential for future solar PV projects are Brazil and Honduras.
Brazil
Although Brazil has always boasted one of the most developed economies in Latin America and has always shown exceptionally large potential for solar energy, it did not show as much solar PV development over the previous years as expected. However, this year has been very fruitful for the country. In June, Brazil announced the commissioning of a gigantic solar project, Lapa Solar park, which has a capacity of 158 MW. At the time that was the third biggest solar PV project in Latin America, trumped only by two other projects, located in Chile.
Things changed drastically in September of 2017 as it was announced that the newly crowned largest solar PV plant in Latin America started operations in Brazil, namely, the Nova Olinda Solar Park, with a capacity of 292 MW. The country also experienced - in the same month - the connection of the second largest solar PV project in Latin America, the Ituverava solar park, with a capacity of 254 MW. September was very prolific for Brazil as it commissioned a total of 546 MW of solar power projects, which has caused its ranking to go up, now claiming two top-3 spots in the Top 50 operational solar power plants. Both projects are owned and operated by Enel Green Power.
Without a doubt, 2017 stands out for Brazil as a milestone year in PV capacity. Adding to all of that success, there is still approximately 530 MW of additional capacity expected to commence operations by the end of 2017. In the meantime, 2018 is looking very promising as well, as a result of more expected growth in PV capacity. Provisional statistics provided by Brazil’s Ministry of Mines and Energy show that there is a planned capacity of 1.34 GW to be connected to the grid in 2018.
Source: Enel Green Power - Lapa Solar Park
Honduras
Honduras has shown to possess many opportunities for solar power development over the past few years. The country was able to start operations in mid-2015 of one of the largest PV projects in the Central American region. The Nacaome and Valle Solar Power Plant comprises 145 MW of solar PV capacity; is owned by Larach Group; and is operated and maintained by Scatec Solar. The plant is located in the southern part of Honduras and is able to provide energy for more than 71.500 households.
According to the annual overview of the state of renewable energy by REN21, Honduras was able to have enough installed solar PV capacity by the end of 2016 to meet 9.8% of its electricity demand. The overview also showed that Honduras was one of the top countries when it comes to investments made in renewable power and fuels relative to its annual GDP. Additionally, Honduras was able to generate 10.2% of its total generated electricity in 2016 with the use of PV power plants. This shows that, when it comes to the development of solar energy, the market of solar PV in Honduras is growing into a major market for the Central American region.
Philippines
In the developing Asian region, the Philippines was ranked number 1 in terms of Top 50-listed operational solar PV projects. The country is still relatively young when it comes to solar development, but was able to get 7 active projects ranked in the top 50 list. The biggest operational project in Philippines at the moment is the Cadiz Solar Power Plant. The 132.5 MW plant was developed by Helios Solar Energy Corp, which is a joint venture between Thailand-based Soleq Solar Co. and Gregorio Araneta Inc., and is owned by Equis Funds Group. The commissioning of this plant solidifies the solar market in the Philippines as being capable of handling such large scale utility projects.
Most of the current projects in the Philippines are smaller than 20 MW, therefore their capacity is not large enough to be ranked in the Top 50 list. However, some companies in Philippines do have plans for larger solar parks for the future.
In March of this year, a Filipino renewable energy company, Solar Philippines, started building a 150 MW solar plant in the Tarlac province with plans for additional battery storage capacity in place. The park is expected to be finished by late 2017, making it the largest solar power project to date for the island nation.
As of June 2017, the Philippines has 900 MW of installed capacity, but has ambitions to keep promoting the establishment of solar value chains in the country. One way that the country wants to achieve this is by opening up its first PV module factory in Santo Tomas, Batangas province. According to Leandro Leviste, the chief executive of Solar Philippines, this factory could help filipinos save up to a 30% on electricity. The developments in the market are promising, but it still needs to be seen how much this will benefit the country as Solar Philippines aims to produce PV modules for the U.S. and European markets.
Thailand
Thailand was able to place in our list at number 12, with the second biggest solar PV project in Asia, the EA Solar Lampang. This solar plant has a capacity of 128 MW, making it the largest solar PV plant in Thailand. The plant was developed and is currently owned by Energy Absolute Public Company. When it comes the total quantity of Top 50 operational projects in Asia, Thailand has the second largest amount of listings, with its 5 active projects.
Over the years, the solar market in Thailand has shown that there are many attractive investment opportunities for players that in the past might not have been interested in solar energy. One such example is Padaeng Industry, an energy and waste management company based in Thailand, that expanded its operations by acquiring a portfolio of solar PV farms with a total capacity of 30 MW. The country’s rising interest in solar energy investment has caused the government to make some adjustments in its policies for the coming years.
Thailand’s government has been very enthusiastic about solar power development and has communicated efforts to revise their Alternative Energy Development Plan, which states that the country aims to promote the use of alternative energy with the objective to cover 25% of the total energy consumption.
Recently, Thailand’s energy policy makers have revised this percentage to 40%, with plans to accomplish the new target by 2036. This new target more than doubles the previously planned capacity for solar PV power-generation from 19.600 MW to 40.000 MW. In order to cope with such an increase in projects, the Energy Regulatory Commission has implemented a new screening policy under which it plans to screen investors for active businesses and disqualify any inactive investor from the current biddings. These measures were taken as a way to prevent investors from obtaining licenses for projects without investing in the actual projects. This was the case in 2016, when investors did not commit to 200 MW worth of projects after the government had already issued the project licenses.
EA Solar Lampang Thailand
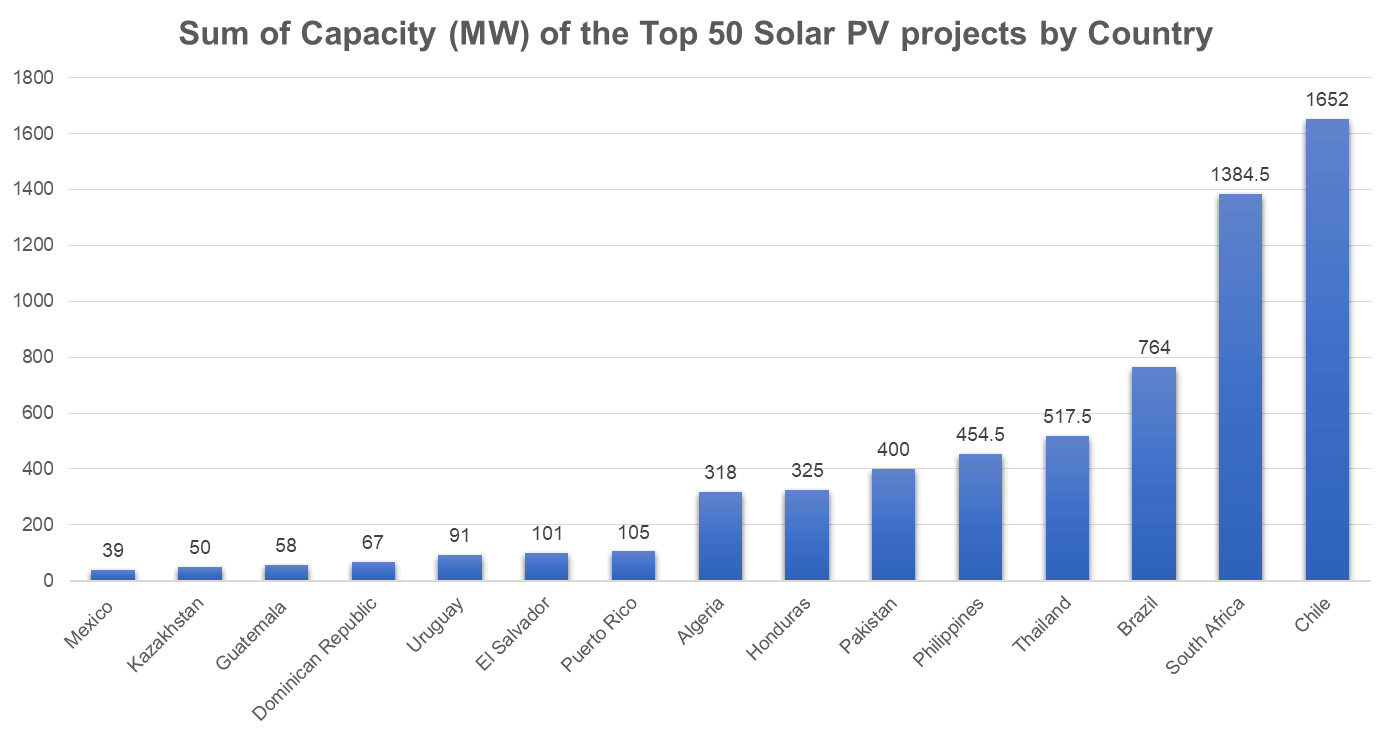
Capacity of Emerging Markets
Summarizing the total ranked capacity within the Top 50 Solar PV projects by country, the Top 5 ranked emerging markets include Chile in the leading position, followed by South Africa coming in as a close second, trailed by Brazil, Thailand and the Philippines.
When comparing the ranking of leading countries in terms of total capacity with the list of leading countries ranked by amount of listed projects some similarities manifest themselves, but also some interesting differences arise. One of those differences is that while Chile and South Africa have the same amount of active Top 50 solar projects, Chile has around 267.5 MW more listed capacity than South Africa.
*This graph does not use the total MW capacity installed by country, but the total MW capacity of the Top 50 Solar PV projects by country.
The dynamics in the solar industry for emerging markets are changing constantly, among other things, as a result of newly commissioned projects or multi-phase projects that commission new MWs of capacity as construction advances. This was the case with Brazil during 2017, where 3 major projects were commissioned in less than 4 months. When compared to our previous report less than a year ago, Brazil moved up from 30 MW of capacity to 764 MW once the solar projects were put into operation.
The situation in Thailand did not change that much since our last report. The country did commission some solar power projects, but on such a small scale that they did not make it to the list. In addition, Thailand is going through some changes in their policy regulations in order to tackle the problem of inactive investors. It still needs to be seen how the market will react to the new screening procedures and the new energy target.
The Philippines, on the other hand, were able to commission 2 new solar plants that made it on our list. Although the country is also going through some policy changes, the solar market has been getting much support from the government and especially the president. The two new operating projects have led Philippines to increase their capacity with 110 MW compared to what was previously reported. The country also has a major project still in the pipeline that could once again increase the MW capacity of the Philippines in the Top 50 list.
For emerging markets, the countries analyzed have shown that they are able to design, construct and operate large scale projects in short time spans in a way that can rival other projects in more developed markets. The situation in some countries is still vulnerable to policy changes, new regulations or political disputes, but most of them have clear objectives when it comes to renewable energy generation. The majority of the new plants featured in the Top 50 were commissioned in the last 6 months, with many other potentially record-breaking projects still under construction. It will be interesting to see how these emerging markets develop over the coming months, as most countries are expected to put a variety of new projects into operation by the end of this year and/or during the first half of next year.